Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, Management Unit of North Sea and Scheldt Estuary Mathematical Models, Belgian Marine Data Centre
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
-
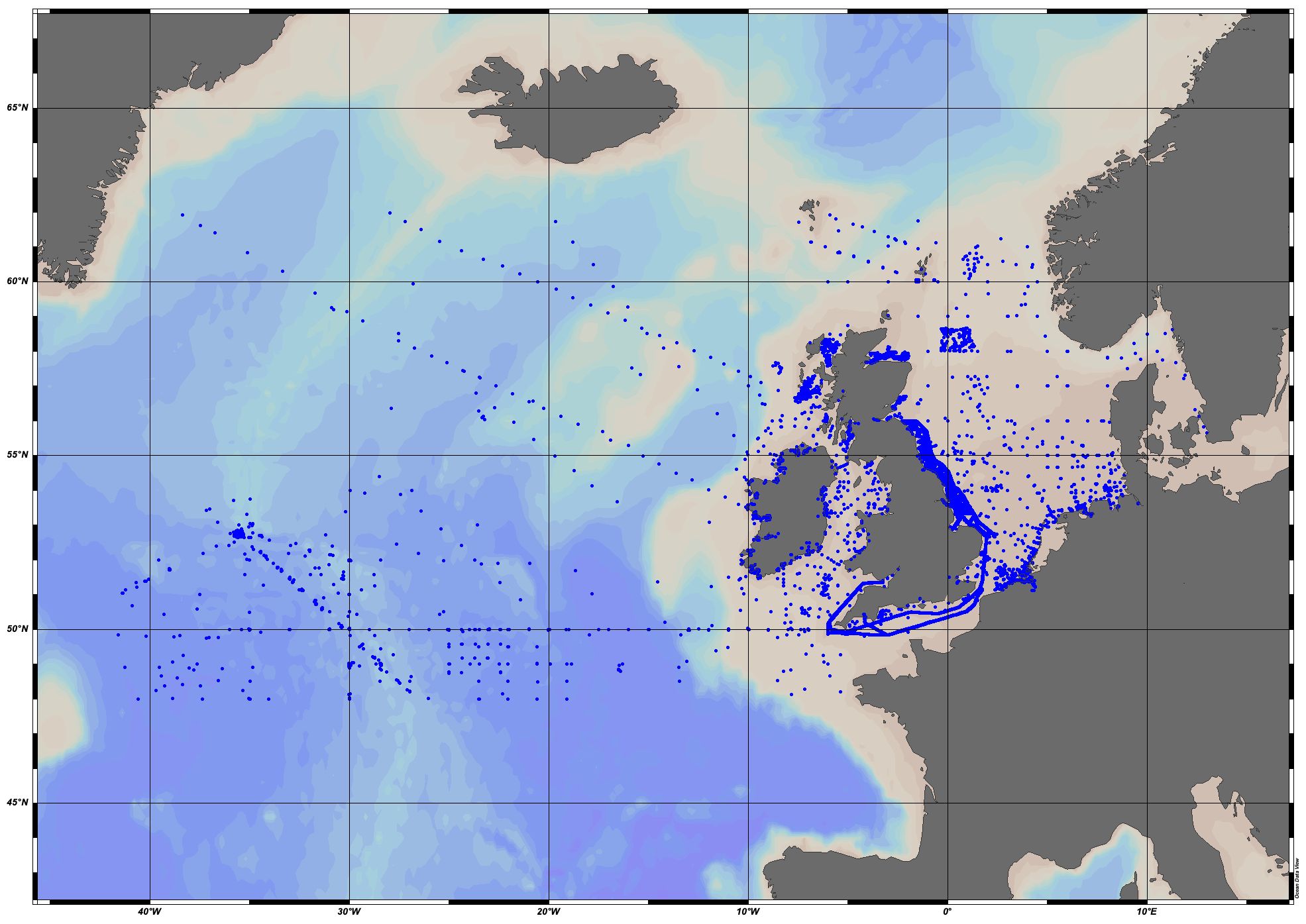
EMODnet Chemistry aims to provide access to marine chemistry datasets and derived data products concerning eutrophication, acidity and contaminants. The importance of the selected substances and other parameters relates to the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This aggregated dataset contains all unrestricted EMODnet Chemistry data on potential hazardous substances, despite the fact that some data might not be related to pollution (e.g. collected by deep corer). Temperature, salinity and additional parameters are included when available. It covers the Greater North Sea and Celtic Seas. Data were harmonised and validated by the 'Aarhus University, Department of Bioscience, Marine Ecology Roskilde' in Denmark. The dataset contains water (profiles), sediment (profiles) and biota (profiles and timeseries). The temporal coverage is 1970–2022 for water measurements, 1970–2021 for sediment measurements and 1979–2022 for biota measurements. Regional datasets concerning contaminants are automatically harvested and the resulting collections are harmonised and validated using ODV Software and following a common methodology for all sea regions ( https://doi.org/10.6092/8b52e8d7-dc92-4305-9337-7634a5cae3f4). Parameter names are based on P01 vocabulary, which relates to BODC Parameter Usage Vocabulary and is available at: https://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/search_nvs/P01/. The harmonised dataset can be downloaded as as an ODV spreadsheet, which is composed of a metadata header followed by tab separated values. This spreadsheet can be imported into ODV Software for visualisation (more information can be found at: https://www.seadatanet.org/Software/ODV). In addition, the same dataset is offered also as a txt file in a long/vertical format, in which each P01 measurement is a record line. Additionally, there are a series of columns that split P01 terms into subcomponents (substance, CAS number, matrix...).This transposed format is more adapted to worksheet applications (e.g. LibreOffice Calc).
-
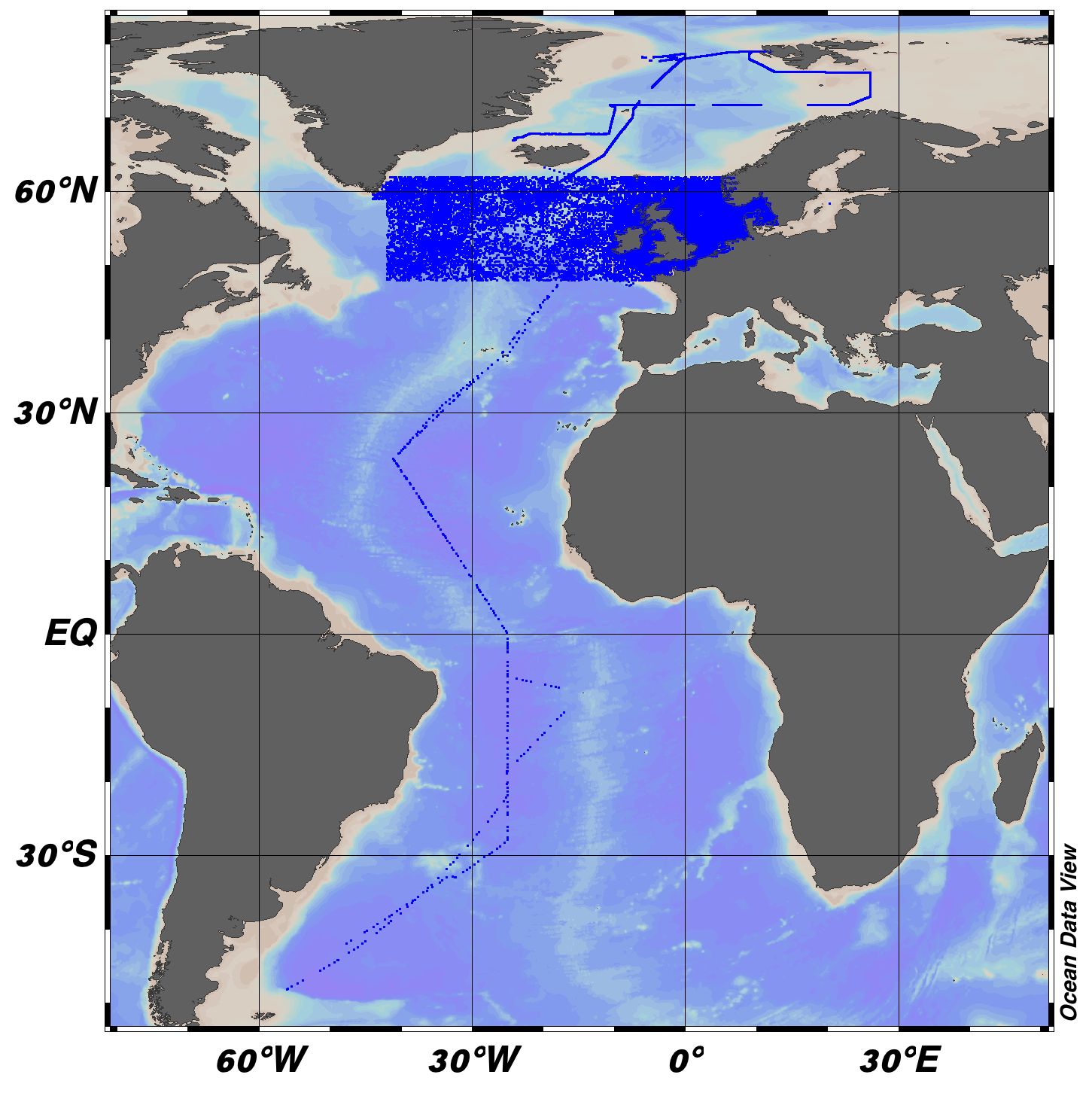
EMODnet Chemistry aims to provide access to marine chemistry datasets and derived data products concerning eutrophication, acidity and contaminants. The importance of the selected substances and other parameters relates to the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). This aggregated dataset contains all unrestricted EMODnet Chemistry data on eutrophication and acidity, and covers the Greater North Sea and Celtic Seas. Data were aggregated and quality controlled by 'Aarhus University, Department of Bioscience, Marine Ecology Roskilde' in Denmark. ITS-90 water temperature and water body salinity variables have also been included ('as are') to complete the eutrophication and acidity data. If you use these variables for calculations, please refer to SeaDataNet for the quality flags: https://www.seadatanet.org/Products/Aggregated-datasets. Regional datasets concerning eutrophication and acidity are automatically harvested, and the resulting collections are aggregated and quality controlled using ODV Software and following a common methodology for all sea regions ( https://doi.org/10.13120/8xm0-5m67). Parameter names are based on P35 vocabulary, which relates to EMODnet Chemistry aggregated parameter names and is available at: https://vocab.nerc.ac.uk/search_nvs/P35/. When not present in original data, water body nitrate plus nitrite was calculated by summing all nitrate and nitrite parameters. The same procedure was applied for water body dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), which was calculated by summing all nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium parameters. Concentrations per unit mass were converted to a unit volume using a constant density of 1.25 kg/L. The aggregated dataset can also be downloaded as an ODV collection and spreadsheet, which is composed of a metadata header followed by tab separated values. This spreadsheet can be imported to ODV Software for visualisation (more information can be found at: https://www.seadatanet.org/Software/ODV).
-
This dataset is a compilation of en-route thermo-salinometry data recorded by the RV A962 Belgica. Data are grouped per campaign from 1993 until 2021. Data are measured by a Sea-Bird thermo-salinometry sensor installed in the vessel Scientific Seawater circuit (constant depth).
-
An analytical method was developed for the trace quantification of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (oxyPAHs) in mussels. Compounds included were naphthalene-1-ol, 9H-fluoren-9-one, anthracene-9,10-dione, 7H-benz[de]anthracene-7-one, naphtacene-5,12-dione and benzo[a]anthracene-7,12-dione. Pyrene-1-carboxaldehyde was applied as an internal standard. Sample extraction by pressurized liquid extraction was followed by clean up on silica, separation by high performance liquid chromatography and quantitative measurement by mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation. The method was validated by the analysis of spiked mussel samples, resulting in trueness values of 90-124% and measurement uncertainties of 6-49%, except for naphthalene-1-ol. Quantification limits varied from 0.25 ng.g-1 to 10.7 ng.g-1. The developed analytical oxyPAH method was applied on mussel samples from groynes and quaysides along the Belgian coastline and oxyPAH data were compared to PAH concentration data. The sum of 14 US EPA priority PAHs reached maxima at the eastern side of the Belgian coastal zone, with on average 202 ng.g-1 for quayside Zeebrugge and 38.4 ng.g-1 for groyne Knokke mussels. Anthracene-9,10-dione concentrations reached maxima of 19.1 ng.g-1 mussels at the most industrialized quayside of Zeebrugge. For other oxyPAHs, no clear relationship could be made with direct PAH emissions. Concentrations of anthracene-9,10-dione and 9H-fluoren-9-one were found to exceed corresponding parent PAH concentrations.
-
The chemical status of five dredged spoil disposal sites in the Belgian Part of the North Sea, near the ports of Ostend and Nieuwpoort, is evaluated. A linear mixed-effect model was applied to PCB, PAH and heavy metal data from 2005-2014. No decrease in PCB concentrations was found, with even an increase at two disposal sites. Hg/AL ratios increased with 62% at one disposal site (BR&WS2) from 2005-2006 to 2013-2014. Cu and Zn concentrations increased at two disposal sites. Additional harbour sampling suggests that the latter is possibly linked to antifouling paints. Based on OSPAR environmental assessment criteria, the current chemical status of the sites suggests no chronic effect of dredged spoil disposal. However, increasing time trend data for PCB, Hg, Cu and Zn demonstrate the importance of monitoring to identify adverse trends.
 EMODnet Product Catalogue
EMODnet Product Catalogue