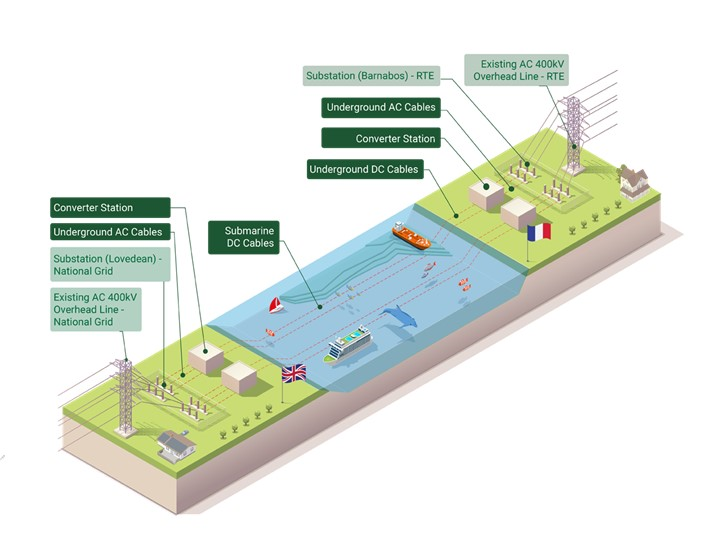
AQUIND Interconnector will provide a new subsea and underground high voltage direct current electric power transmission link between France and England. This new link has the intention to improve the security of energy demands and reduce carbon emmissions whilst also allowing power grids to become more flexible as they adapt to sources of renewable energy.
Due to the nature of the project involving the installation of a sub-seabed cable, an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) scoping report is required prior to approval and subsequent EIA assessment. A scoping report is required to identify regions that might be impacted by the installation and where mitigation measures are required. Such a report requires extensive onshore and offshore surveys to be conducted in order to plan the best route for the cable and in order to identify regions which will be affected by its installation. Surveys include geophysical, geotechnical and benthic ecology surveys in order to identify sediment types and structures, seabed ecology and presence of anthropogenic debris.
EMODnet Seabed Habitat’s broad-scale predictive habitat map for Europe (EUSeaMap 2019) provided EUNIS habitat information that enabled AQUIND to identify the main habitat types reported in the region that intersects the proposed cable route. Such datasets are essential to assess potential impacts on habitats and plan mitigation strategies to resolve these. EMODnet offers a high quality open-source integrated and harmonised dataset which has increased the industries awareness of habitat types during the early stages of planning and thus ensuring the open communication of potential environmental impacts during various consultation stages of this development. These data are invaluable to industries involved in marine infrastructure and ensures the transparency of large-scale developments and their associated potential impacts to interested parties, thus ensuring the conservation of important marine ecosystems.
This EIA scoping report has identified two main habitat types (high energy shallow circalittoral coarse sediment and moderate energy deep circalittoral coarse sediment) which will intersect with the proposed cable development. Potential impacts from a high voltage direct current cable include habitat loss, electro-magnetic field emmissions, heat emmission, deposition of sediment and impacts from resuspension of (contaminted) sediment. These potential impacts can now be assessed and mitigation measures provided during future EIA assessment based on the likelihood of such impacts occuring.
© Aquind
